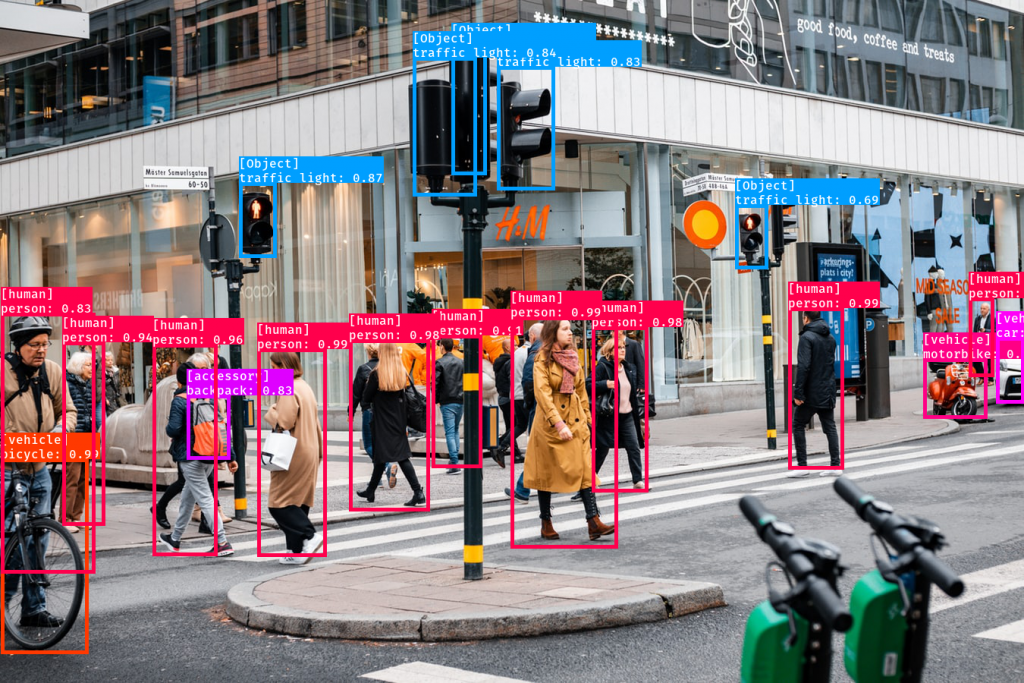
You can use the Nvision’s Object Detection service to detect labels in an image. this service localizes and identifies multiple objects in the image such as people, animals, vehicles, and furniture. see machine learning services.

A response is returned in JSON format similar to the following example:
{
"detected_objects": [
{
"confidence": 0.8327999711036682,
"parent": "accessory",
"bounding_box": {
"left": 246,
"right": 303,
"top": 520,
"bottom": 605
},
"name": "backpack"
},
...
{
"confidence": 0.6195999979972839,
"parent": "Object",
"bounding_box": {
"left": 595,
"right": 641,
"top": 64,
"bottom": 230
},
"name": "traffic light"
}
]
}
If you have not created a Nvision service account credentials, do so now in this set up the Nvision API quickstart for instructions.
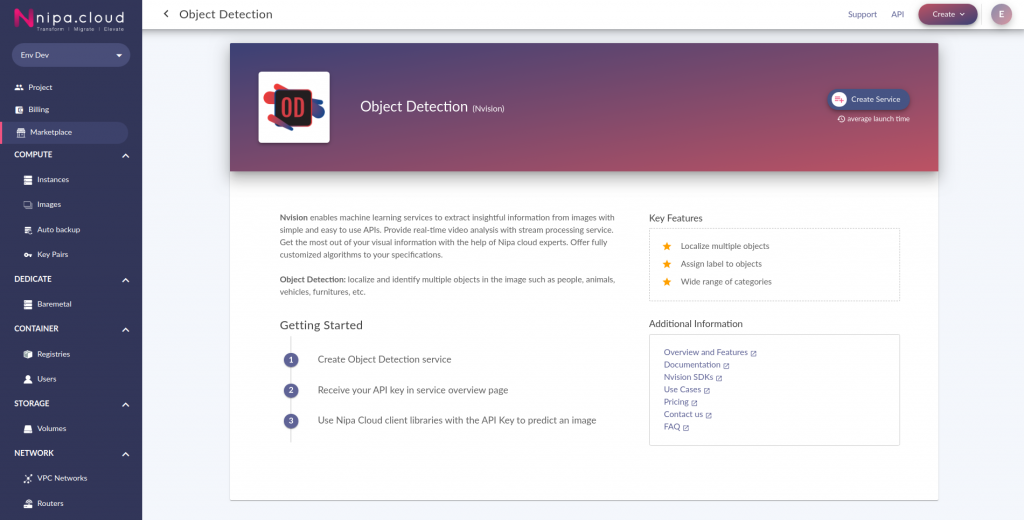
Once your service has been created, go to the service overview page under API Key to get your service key.
Detect objects in an image
Image Content
The Nvision API can perform object detection on a local image file by sending an image as a base64 encoded string in your request body.
The base64 encoded string is a binary-to-text encoding that represents binary data in an ASCII string format as the following example: /9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQEBLAEsAAD...
JSON Request Body
The API is accessible via the HTTP method and URL:
POST https://nvision.nipa.cloud/api/<<service_name>>
{
"raw_data": <<BASE64_ENCODED_IMAGE>>,
"configurations": [
{
"parameter":"OutputCroppedImage",
"value":"false"
},
{
"parameter": "ConfidenceThreshold",
"value": "0.1"
}
]
}
The configuration is different on individual service types. It is structured as a key-value mapping. A config name is defined in parameter field and the corresponding value is defined in value field in string format.
For object detection service, there are two available configurations as follows:
OutputCroppedImage: to return cropped images from bounding box detections.- Value options:
"true"or"false" - Default:
"false"
- Value options:
ConfidenceThreshold: to define the minimum confidence score of the prediction results.- Value options:
[0, 1] - Default:
"0.1"
- Value options:
Making a RESTful Call
You can call this API through REST calls or native SDKs.
Send the request using the cURL command line
export API_KEY="<<YOUR_API_KEY>>"
# save the json request body as a file named request.json
curl -X POST \
https://nvision.nipa.cloud/api/object-detection
-H 'Authorization: ApiKey '$API_KEY \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8' \
-d @request.json | json_pp
# or read a local image from filepath
echo -n '{"raw_data": "'"$(base64 image.jpg)"'"}' | \
curl -X POST \
https://nvision.nipa.cloud/api/object-detection \
-H 'Authorization: ApiKey $API_KEY' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-d @- | json_pp
Send the request using the client libraries
Nvision SDKs provide interface for calling Nvision services in your own language, see the API Reference, in this guide, covers calling Nvision API for Python and JavaScript.
Installation
- For python, using pypi package here: https://pypi.org/project/nvision/
- For nodejs, using npm package here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nipacloud/nvision
# Python pip install nvision # JavaScript npm i @nipacloud/nvision
Python SDK
import os
import json
import base64
from nvision import ObjectDetection
model = ObjectDetection(api_key='YOUR_API_KEY')
# base64 encoed string
with open('image.jpg', 'rb') as file:
image = file.read()
image = base64.b64encode(image).decode('utf-8')
# make a RESTful call to the Nvision API
response = model.predict(image)
# get the predictions (in JSON format) from the response
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=4, sort_keys=True))
JavaScript SDK
javascript example
Detect Object in a video
An example of how to integrate @nipacloud/nvision SDK to the frontend app.
https://github.com/nipa-cloud/nvision-browser-example
To set up the SDK with Webpack
Nvision SDK comes with a built-in TypeScript definition. You can configure Webpack alias to point to the browser variant of the library.
{
...
resolve: {
alias: {
"@nipacloud/nvision": "@nipacloud/nvision/dist/browser/nvision.js"
}
}
...
}